2H₂g O₂g 2H₂Og The mole ratio between O₂ and H₂O is 1 mol O₂2 mol H₂O. For example in the reaction.
Determine the mass in grams of C2H6O necessary to produce 120 g CO2 in the following reaction.
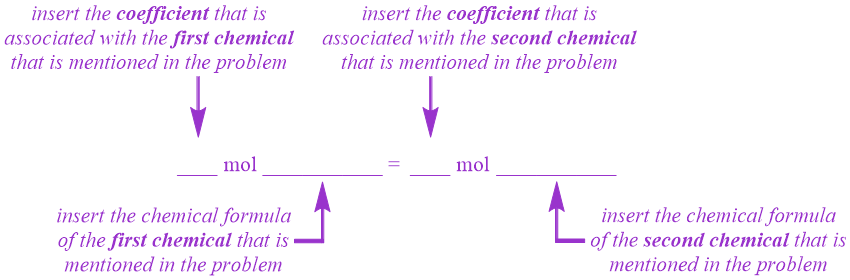
. Molar quantity of the unknown. There are four steps in solving a stoichiometry problem. This conversion requires the use of the molecular weight.
We used the Number and Brightness technique N and B which relies on the RICS image acquisition to investigate the oligomeric state of the SHR protein. A balanced chemical equation allows one to determine the. Determine the volume at equivalence then divide by 2 to calculate the volume at half-equivalence.
Almost all stoichiometric problems can be solved in just four simple steps. Write the balanced chemical equation. Sornaraj et al 2016.
Lets Answer The World. For any balanced chemical reaction whole numbers coefficients are used to show the quantities generally in moles of both the reactants and products. Total number of reactants in a chemical equation D.
First calculate the number of moles of CO2 that are produced. The coefficients in the balanced equation are used to derive stoichiometric factors that permit computation of the desired quantity. Which of the following stoichiometric factors would be used to convert from moles of NH 3 to moles of H 2 O for the reaction.
10 3 moles Mass of one mole kmole is a number of grams. The conversion factor used to convert from grams to moles is _____. 6 October 2021 by lets tokmak.
Select the correct answer below. The easiest way to do stoichiometric calculations involves using conversion factors. Applying Conversion Factors to Stoichiometry Now youre ready to use what you know about conversion factors to solve some stoichiometric problems in chemistry.
The Haber process for producing ammonia commercially is represented by the equation N2 3H2 ---- 2NH3. A 5 mol O 2 4 mol NH 3. Determine the p K a from this graph following the method demonstrated in Figure 1.
4NH 3 5O 2 4NO 6H 2 O. 120gCO21molCO244009gCO2027267molCO2 Next use a ratio to solve for the number of moles of C2H6O that are required. Rinse the pH electrode with bottled water shake gently and return it to its protective.
This relationship is made using the appropriate stoichiometric factor or mole ratio. Balanced chemical equations are used in much the same fashion to determine the amount of one reactant required to react with a given amount of another reactant or to yield a given amount of product and so forth. While the above example was relatively simple to do in your head it could have been written out mathematically.
Which is defined in relation to the 112 of carbon 12 6C. Convert the units of the given substance A to moles. 112 12 6C 166 10-27 kg Atoms and molecules mass is defined in atomic unit mass.
For example the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen gas to form water can be represented by the balanced equation. Mole ratios are used as conversion factors between products and reactants in stoichiometry calculations. Use a ruler to find the inflection point of the titration curve.
Here are some examples of conversion factors. D 6 mol H 2 O4 mol NH 3. Coefficients in a balanced chemical equation B.
Total number of products in a chemical equation. Stoichiometry is an important feature of protein complexes as some transcription factors must form higher order complexes in order to function Nakashima et al 2012. The method of factor analysis is used to determine the number of reactions and derive an observed stoichiometric space from measured composition and possibly thermal data.
Thus the grams of methane must be converted to moles of methane. Stoichiometry is not only used to balance chemical equations but also used in conversions ie converting from grams to moles using molar mass as the conversion factor or from grams to milliliters using density. A conversion factor is ALWAYS equal to 1.
Coefficients in an unbalanced chemical equation C. C 4 mol H 2 O6 mol NH 3. Use the mole ratio to calculate the moles of wanted substance B.
Balanced chemical equations are used in much the same fashion to determine the amount of one reactant required to react with a given amount of another reactant or to yield a given amount of product and so forth. Stoichiometry is the field of chemistry that is concerned with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. For example when oxygen and hydrogen.
Which of the following conversion factors should you use to complete the calculation. The coefficients in the balanced equation are used to derive stoichiometric factors that permit computation of the desired quantity. B 4 mol NH 3 6 mol H 2 O.
The mole ratio between H₂ and H₂O is 2 mol H₂2 mol H₂O. How many moles of O₂ are required to form 500 moles of H₂O. If the given information is in a unit other than moles the first step in the problem will be to convert this amount to moles.
You use a series of conversion factors to get from the units of the given substance to the units of the wanted substance. Convert units of a given substance to moles. The conversion factor that is always used in stoichiometry problems is the mole to mole ratio for elements or compounds in the balanced equation.
Which of the following is used to determine stoichiometric factors. Which of the following is used to determine stoichiometric factors. Moles and kilomoles Atomic unit mass.
Avogadro number 602210 23 atoms Volume of 1 mole perfect gas 22414 l T 0 oC p 1 atm Kmole. A conversion factor is a ratio or fraction which represents the relationship between two different units. Mole ratio of any two substances in the reaction.
The coefficients in the balanced equation are used to derive stoichiometric factors that permit computation of the desired quantity. Balanced chemical equations are used in much the same fashion to determine the amount of one reactant required to react with a given amount of another reactant or to yield a given amount of product and so forth. Molar quantity of the given substance In a stoichiometric calculation to determine the mass of one substance that will react with a given amount in moles of a second substance you need to know.
TF Stoichiometry problems can be solved with conversion factors created from mole ratios molar masses and Avogadros nunber. A stoichiometric factor gives a mathematical approach to looking at these types of problems. Another conversion factor that is commonly used in stoichiometry is the molar mass or gmol.
For example to find the amount of NaCl sodium chloride in 200 g one would do the following. The stoichiometric factor will always have the same form with the. Inverted molar mass In the following stoichiometry problem how many moles of oxygen are produced when 30 mol of KClO3 decompose completely.
Move mouse over terms in equation.

Reaction Stoichiometry Boundless Chemistry

Reaction Stoichiometry Boundless Chemistry
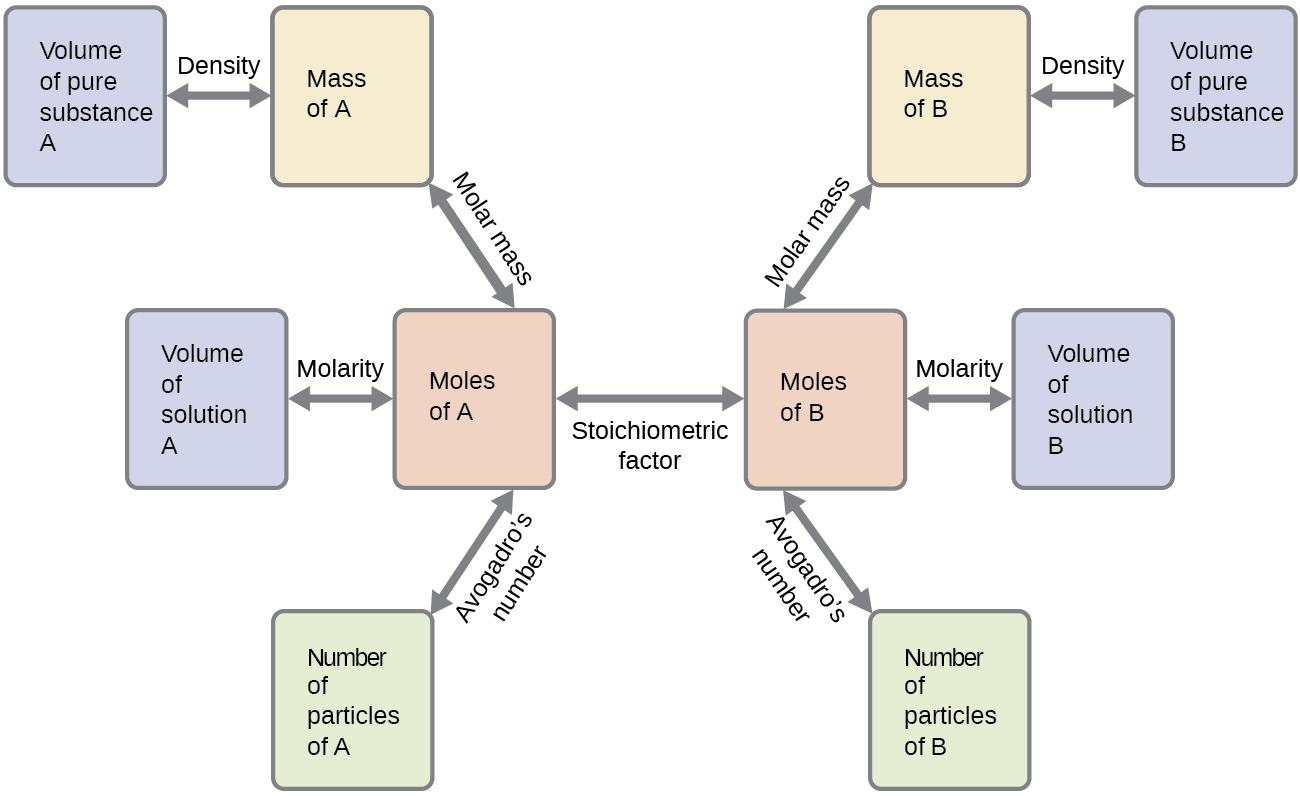
4 3 Reaction Stoichiometry Chemistry

Reaction Stoichiometry Boundless Chemistry
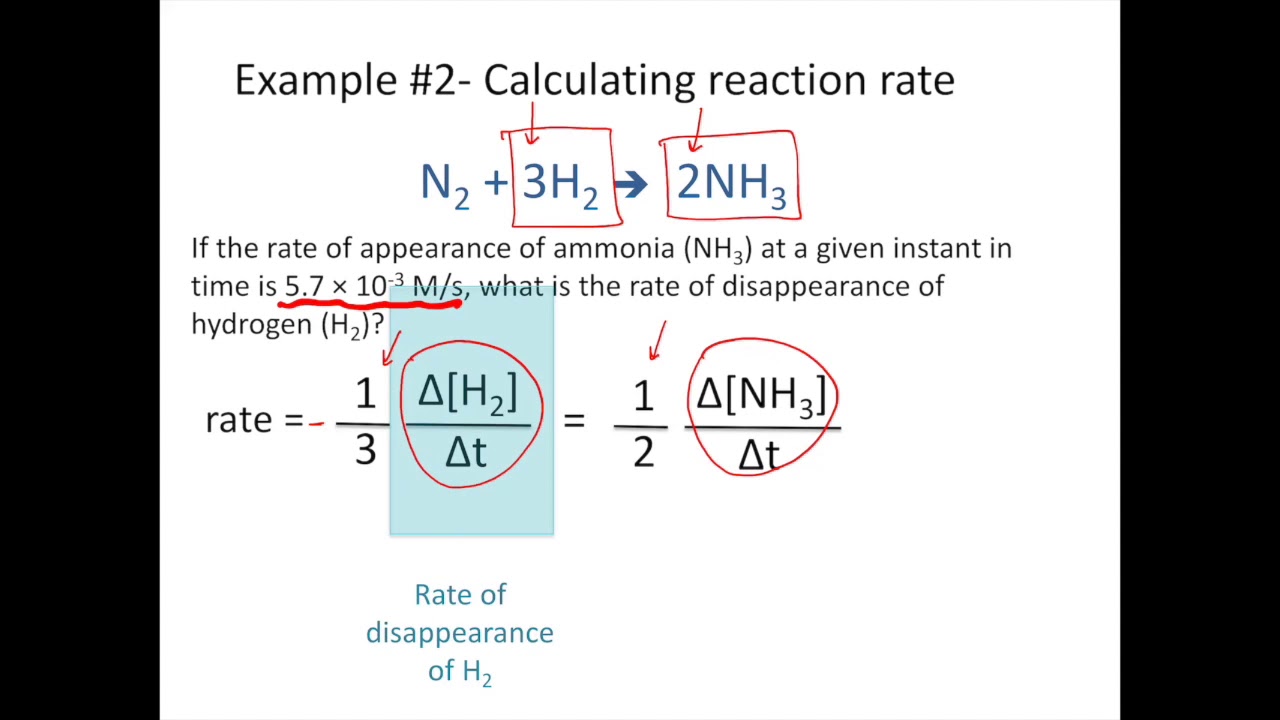
Reaction Rates And Stoichiometry Chemistry Tutorial Youtube
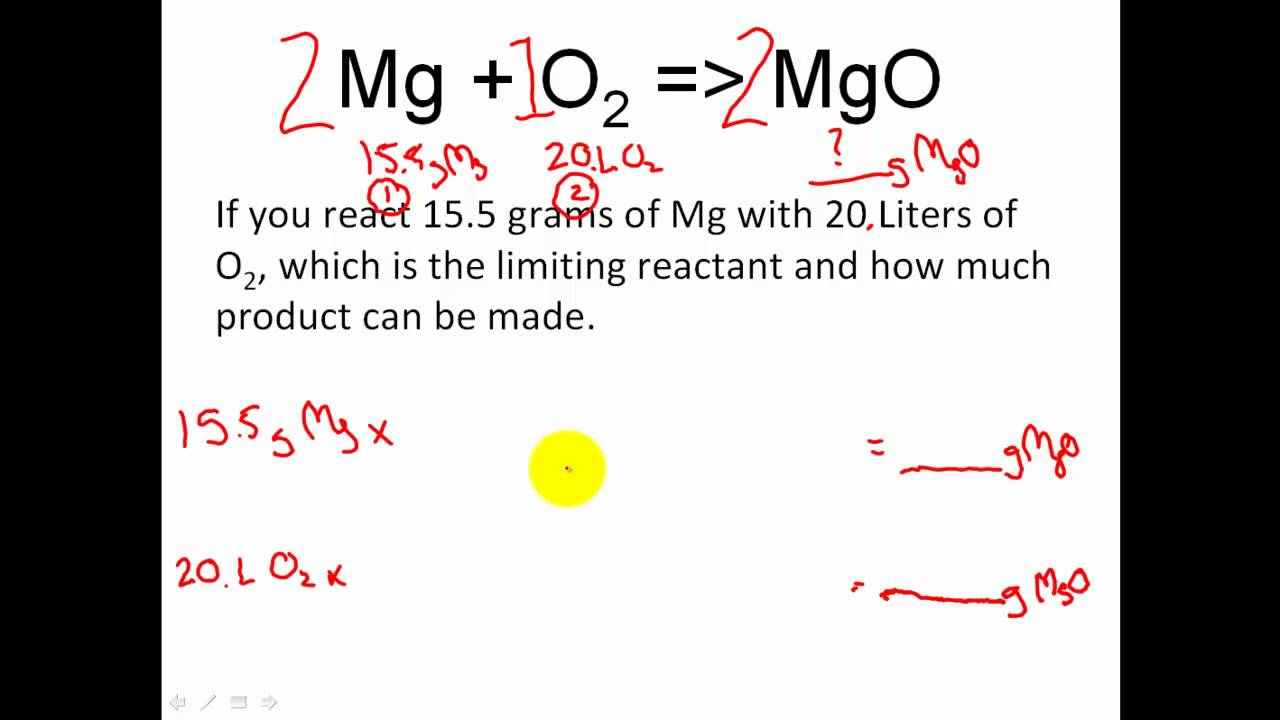
Reaction Stoichiometry Boundless Chemistry

Introduction To Limiting Reactant And Excess Reactant Science Sciencewithtylerdewitt Tylerdewitt Tu Chemistry Help Apologia Chemistry High School Chemistry

Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Pages Intro To Stoichiometry All Stoichiometric Calculations Start With A To Solve You Ppt Download

4 26 Stoichiometry Equality Pattern And Conversions Chemistry Libretexts

0 Comments